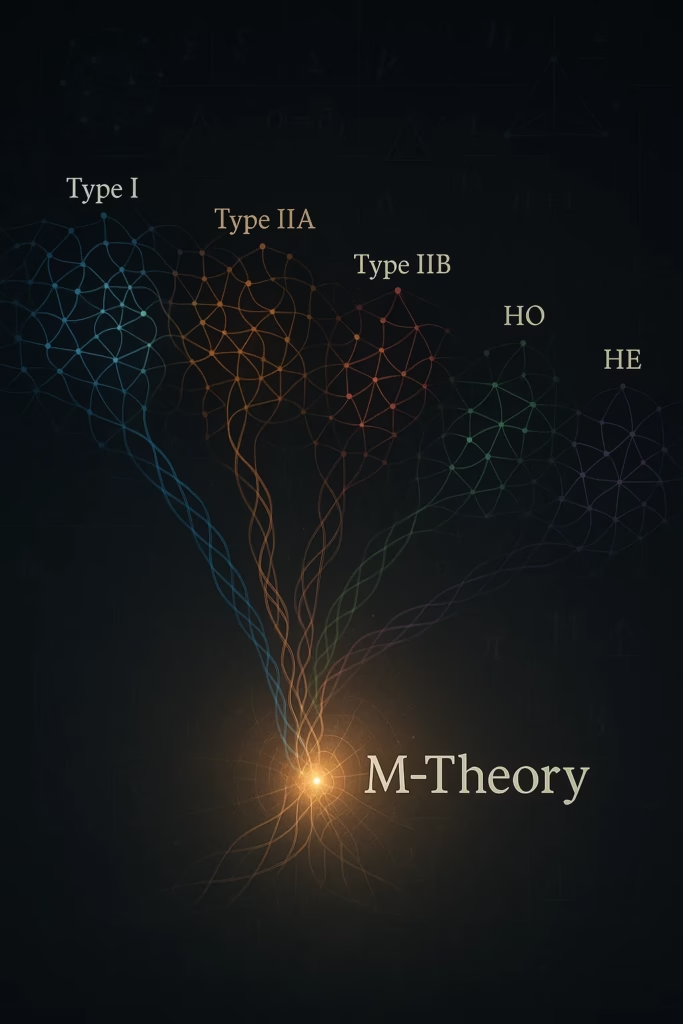
Introduction: Five Paths in the Dark 🗺️
Imagine entering a labyrinth with five different entrances. Each leads through different corridors, different obstacles, and even seems to lead to completely different destinations. Until the 1990s, this is exactly what was happening in theoretical physics – there were five different string theories, each with its own equations, its own rules, its own approach.
Physicists were divided. Was Type IIA the “real” theory? Maybe Heterotic E8×E8? Or one of the other three? It was like looking at the same city through five different rooms – each room has a different window, a different viewing angle, a different perspective.
The First Breakthrough: T-Duality – When Big Becomes Small 🔄
The discovery of T-duality was like the first passageway between rooms in that labyrinth.
What is it actually?
Imagine looking through a camera lens. When you zoom out to a wide angle – you see a large space with small details. When you zoom in to telephoto – you see a small part of space with enormous details. T-Duality states that a string theory with a large compact dimension of radius R is equivalent to a theory with a small dimension of radius 1/R.
A practical example:
- Type IIA theory with a large dimension = Type IIB theory with a small dimension
- As if a large circle and a small circle describe the same geometry
That was the first sign: “Wait… these two theories are actually the same thing!”
The Second Bridge: S-Duality – When Strong Becomes Weak ⚡
While T-Duality connected theories through space, S-Duality established a connection through the strength of interactions.
Analogy:
Imagine looking at a river from two different hills. From one hill, the river looks calm and slow. From the other hill, the same river looks fast and turbulent. S-Duality says that a theory with a strong interaction can be the same as a theory with a weak interaction.
Concretely:
- Type I theory with strong interaction = Heterotic O(32) with weak interaction
- Type IIB theory is self-dual – like a mirror reflecting itself
Witten’s Moment of Enlightenment: The Map of All Maps 🗺️🌟
In 1995, at a conference in Southern California, Ed Witten had his legendary moment. He realized that these two dualities – T and S together – formed a complete set of connections linking all five theories.
It was as if he had found the main control panel that shows how all the rooms in the building are interconnected. M-theory became that overarching framework – the “Theory of all string theories.”
But there was another surprising consequence…
Where Did the Eleventh Dimension Go? 🔍
In the 1980s, physicists had discarded 11-dimensional supergravity theory, considering it a dead end. Witten showed that it was actually the key waiting for its lock.
The discovered connection:
M-theory at low energies → 11-dimensional supergravity
Just as Newtonian mechanics is a limit of Einstein’s relativity
It was a revolutionary understanding: the theory we discarded wasn’t wrong – we just misunderstood it!
What Is M-Theory, Actually? 🔮
The letter “M” remains deliberately undefined:
- Membrane – because it introduces 2D and higher-dimensional objects
- Magic – because of the incredible unification
- Mystery – because we are still searching for its fundamental equations
- Matrix – according to newer interpretations
M-theory tells us that strings were just the tip of the iceberg. There are also 2-dimensional membranes, 3-dimensional objects… a whole zoo of exotic entities.
New Dimensions of Conceptual Understanding 🧩
The Holographic Principle: 💿
M-theory paved the way for one of the most radical ideas in physics – that information in 3D space might live on its 2D surface, like a hologram.
Cosmological Implications: 🌌
The concept of brane collisions promises a new understanding of the Big Bang – perhaps our universe was born from the collision of two branes in a higher-dimensional space.
Experimental Challenges and Hopes 🔬
Although we are still waiting for the final equations, M-theory already:
- Predicts supersymmetry that we are searching for in accelerators
- Provides a framework for understanding dark energy
- Explains why gravity is so much weaker than other forces
Why Do We Need This Today? 💫
Although M-theory still awaits its final equations, its contribution is invaluable:
✅ It showed the unity of nature at the deepest level
✅ It inspired new branches of mathematics
✅ It changed our understanding of space, time, and matter
✅ It opened the path for the holographic principle – the idea that our 3D world might be lived on the surface of a 2D space
✅ It offered a framework for unifying quantum mechanics and general relativity
Concluding Thought: A Journey That Continues 🚀
M-theory shows us that scientific truth is often not about finding new details, but about recognizing the connections between what we already know. Witten’s genius was not in creating something completely new, but in perceiving unity in what seemed like chaos.
As one physicist said: “M-theory is the most beautiful theory we have, even if we don’t yet know exactly what it is.”
What’s Next? 🔭
While we await new experiments and mathematical discoveries, M-theory teaches us an important lesson: sometimes the path to truth is through recognizing unity in apparent diversity – a lesson that applies not only to physics but also to our view of the world around us.
Leave a Reply